As “Which of the following statements is false regarding prostate cancer?” takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
Prostate cancer is a prevalent disease among men, with a significant impact on their health and well-being. Understanding the true nature of this condition is crucial, and this article aims to dispel common misconceptions and provide accurate information.
Prostate Cancer Overview
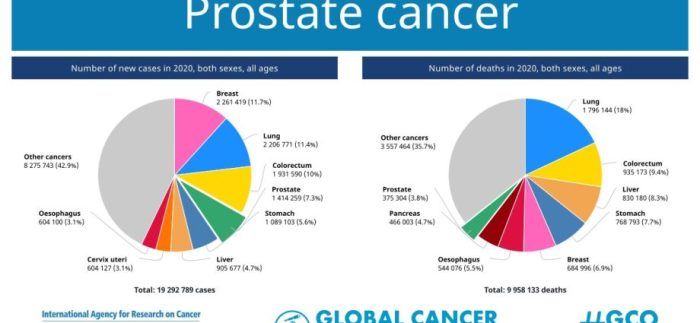
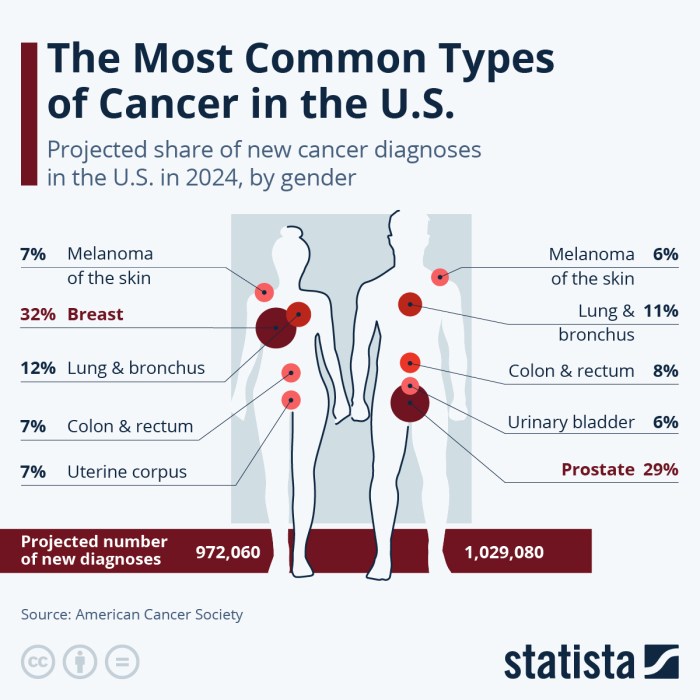
Prostate cancer is a malignant growth that develops in the prostate gland, a small organ located just below the bladder in men. It is the most common cancer among men worldwide, excluding non-melanoma skin cancer. Prostate cancer typically affects older men, with the risk increasing significantly after the age of 50.
Common Symptoms and Signs: Which Of The Following Statements Is False Regarding Prostate Cancer
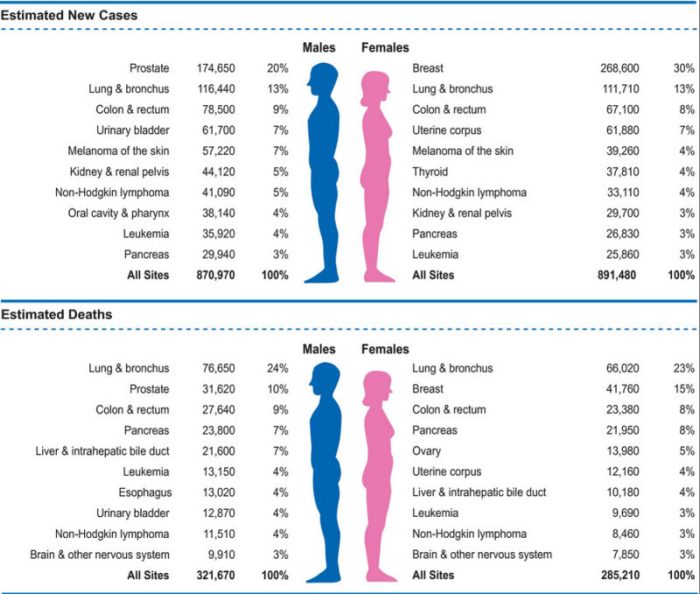
Early-stage prostate cancer often presents with no noticeable symptoms. As the cancer progresses, it may cause urinary problems, such as difficulty starting or stopping urination, frequent urination, or a weak or interrupted urine stream. Other symptoms may include pain or discomfort in the lower back, pelvis, or thighs; erectile dysfunction; and blood in the urine or semen.
Risk Factors and Causes
Age is the most significant risk factor for prostate cancer, with the incidence increasing with advancing age. Family history also plays a role, as men with a father or brother who had prostate cancer are at a higher risk of developing the disease.
Other risk factors include race, ethnicity, and lifestyle choices such as obesity and a diet high in saturated fats.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Prostate cancer is typically diagnosed through a combination of tests, including a physical exam, a blood test to measure prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels, and a biopsy to confirm the presence of cancer cells. Treatment options vary depending on the stage and grade of the cancer, and may include surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, or a combination of these approaches.
Myths and Misconceptions, Which of the following statements is false regarding prostate cancer
There are several common myths and misconceptions surrounding prostate cancer. One is that it is an inevitable part of aging, which is not true. While the risk of prostate cancer does increase with age, it is not an unavoidable condition.
Another misconception is that alternative therapies can cure prostate cancer, which is not supported by scientific evidence.
Prostate Cancer Screening
Prostate cancer screening is recommended for men over the age of 50 who are at average risk of developing the disease. Screening involves a blood test to measure PSA levels and a digital rectal exam. The benefits and limitations of screening should be discussed with a healthcare professional before making a decision about whether or not to undergo screening.
Impact on Quality of Life
Prostate cancer can have a significant impact on a man’s quality of life, both physically and emotionally. Treatment side effects, such as urinary incontinence or erectile dysfunction, can affect daily activities and relationships. Men with prostate cancer may also experience anxiety, depression, or other emotional challenges.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research efforts in prostate cancer are focused on developing new diagnostic techniques, improving treatment outcomes, and reducing the risk of developing the disease. Researchers are also exploring the potential of personalized medicine and targeted therapies to tailor treatment to individual patients.
Helpful Answers
Is prostate cancer always fatal?
No, prostate cancer is often treatable, especially when detected early. With advancements in medical care, many men can live long and fulfilling lives after a prostate cancer diagnosis.
Is a PSA test the only way to detect prostate cancer?
No, while PSA testing is commonly used, other methods such as digital rectal exams and biopsies may also be employed for accurate diagnosis.
Can prostate cancer be prevented?
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent prostate cancer, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, may reduce the risk.